What is Acute Coronary Syndrome
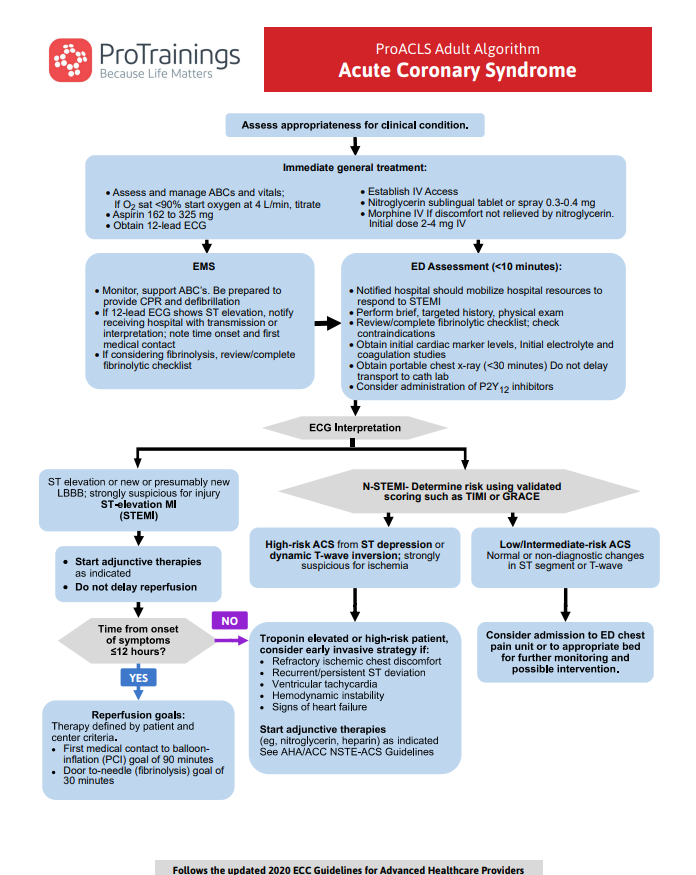
An initial 12-lead ECG is used as part of the identification process for all acute coronary syndrome (ACS) cases.
The three ECG categories for acute coronary syndrome include:
- ST segment elevation, suggesting an active acute myocardial infarction (AMI)
- ST segment depression, suggesting ischemia
- Non-diagnostic/normal ECG
STEMI (ST elevation myocardial infarction) is the focus of this section, since it is the most time-sensitive for reperfusion therapies. Early treatment can limit the amount and extent of myocardial damage.
The main goal of a STEMI ACS is to reperfuse the myocardial tissue that is being damaged by a blockage. Reperfusion may involve the use of coronary angiography with balloon angioplasty and stenting, known as percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). When PCI is used as the initial reperfusion treatment for STEMI, it is referred to as primary PCI.
Acute Coronary Syndrome Treatment
Treatments other than primary PCI include but are not limited to:
- Oxygen
- Aspirin (ASA)
- Nitroglycerin (sublingual tablet or spray)
- Fibrinolytic therapy
- Heparin – UFH (unfractionated Heparin) or LWMH (low-molecular-weight Heparin)
Adult Acute Coronary Syndrome Algorithm