To gain an understanding of what is “normal”, we will examine a sinus rhythm. This type of rhythm is defined as any cardiac rhythm where depolarization of the cardiac muscle begins at the sinus node. It is characterized by the presence of correctly-oriented P waves on the electrocardiogram (ECG).
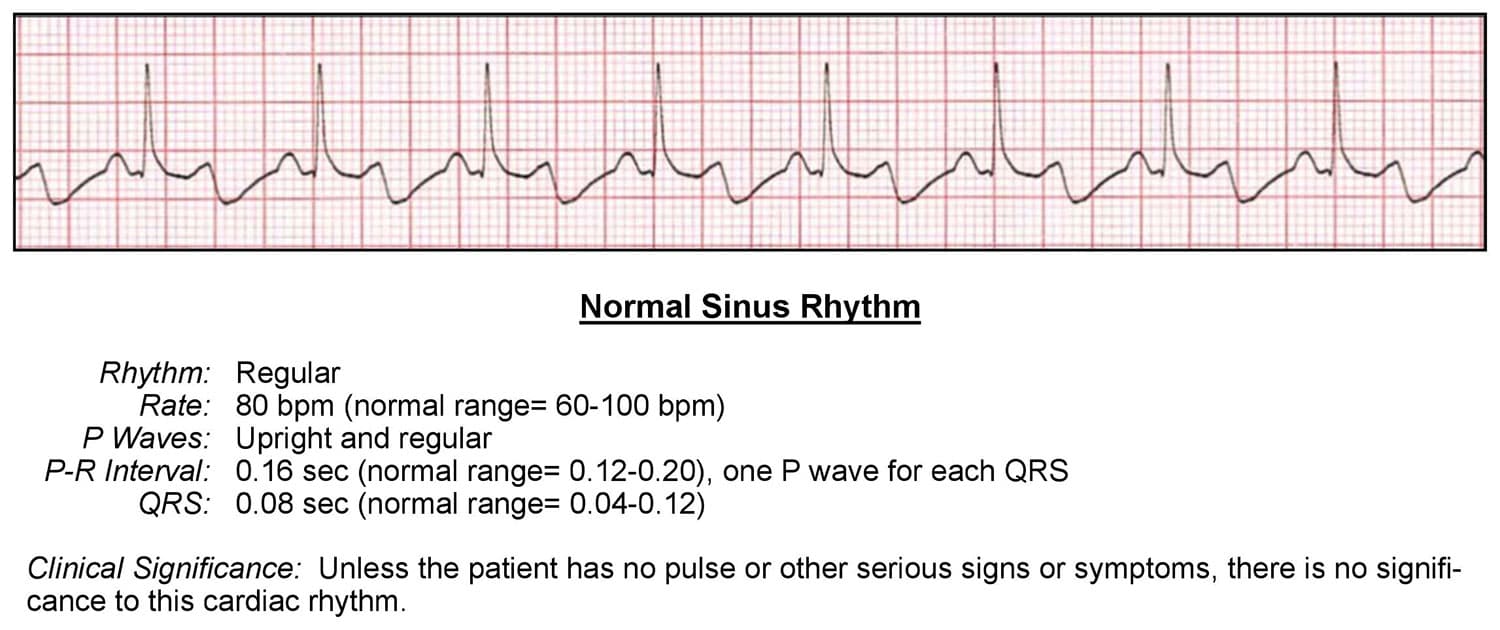
Here is an example of evaluating a normal sinus rhythm:
Rhythm:
- Is the rhythm regular or irregular?
- It’s regular
Rate:
- What is the rate?
- 80bmp
- Is the rate normal, fast or slow?
- Normal, because the rate is between 60-100 bpm
P Waves:
- Are they present?
- Yes
- Do they occur regularly?
- Yes
- Is there one P wave for each QRS complex?
- Yes
- Are the P waves smooth, rounded, and upright?
- Yes
- Do all P waves have similar shapes?
- Yes, each has a uniform shape and are smooth and rounded.
PR Interval:
- Is the PR interval constant?
- Does the PR interval fall within the normal 0.12-0.20 seconds?
- Yes, because the PR interval is contained within one large box which equals .2 seconds
- Is the PR interval constant?
- Yes
QRS Complex:
- Is the QRS interval less than 0.12 seconds?
- Yes, as long as the QRS fits within 2 small boxes and is no larger than 3 small boxes, the QRS is within normal range
- Is the QRS wide or narrow?
- In this case, the QRS is narrow
- Are the QRS complexes similar in appearance?
- Yes
The cardiac interpretation is that this rhythm is a Normal Sinus Rhythm, because:
- The P waves look normal
- Each P wave is followed by a QRS complex
- The PR interval is less than .20 seconds
- The QRS is less than .12 second.
Unless the patient has no pulse or other serious signs or symptoms, there is no clinical significance to this cardiac rhythm.