Note: Your progress in watching these videos WILL NOT be tracked. These training videos are the same videos you will experience when you take the full ProACLS program. You may begin the training for free at any time to start officially tracking your progress toward your certificate of completion.
Atrial fibrillation (also called AFib or AF) is a quivering or irregular heartbeat (arrhythmia) that can lead to blood clots, stroke, heart failure, and other heart-related complications.
In this lesson, we'll look at the three types of atrial fibrillation and then look at a typical ECG readout for an adult patient in AFib and provide a cardiac interpretation. And at the end of the lesson, we'll look at some common causes and side effects of AFib in adult patients.
The Three Types of Atrial Fibrillation
1. Paroxysmal
Paroxysmal, or transient atrial fibrillation, is defined by the following:
- Episodes that stop on their own
- Episodes that last anywhere from seconds to minutes, hours, or even up to one week
2. Persistent
Persistent atrial fibrillation is defined by the following:
- Episodes that last longer than one week
- Episodes that last less than one week but are only stopped using either pharmacological intervention or electrical cardioversion
3. Long-Standing Persistent
Long-standing persistent atrial fibrillation, formerly known as chronic or permanent atrial fibrillation, is defined as episodes that last longer than a year.
Atrial fibrillation occurs when multiple electrical impulses are being generated in the atria and at the same time, which causes chaotic myocardia responses.
AFib can diminish the preload and effectiveness of the cardiac contractions. This action could then cause the development of microemboli due to stagnant blood flow from the atria. In certain instances, this will even lead to a rapid ventricular response that's secondary to a reentry problem.
Pro Tip: The electrical pattern on an ECG will have no discernible P-waves, but instead, will show fibrillatory waves between each QRS complex. And because there's a lack of coordinated electrical impulses generated from the atria traveling through the AV node into the ventricles, the result is usually an irregular ventricular response, which also occurs irregularly.
Now let's take a look at an ECG for an adult patient in atrial fibrillation.
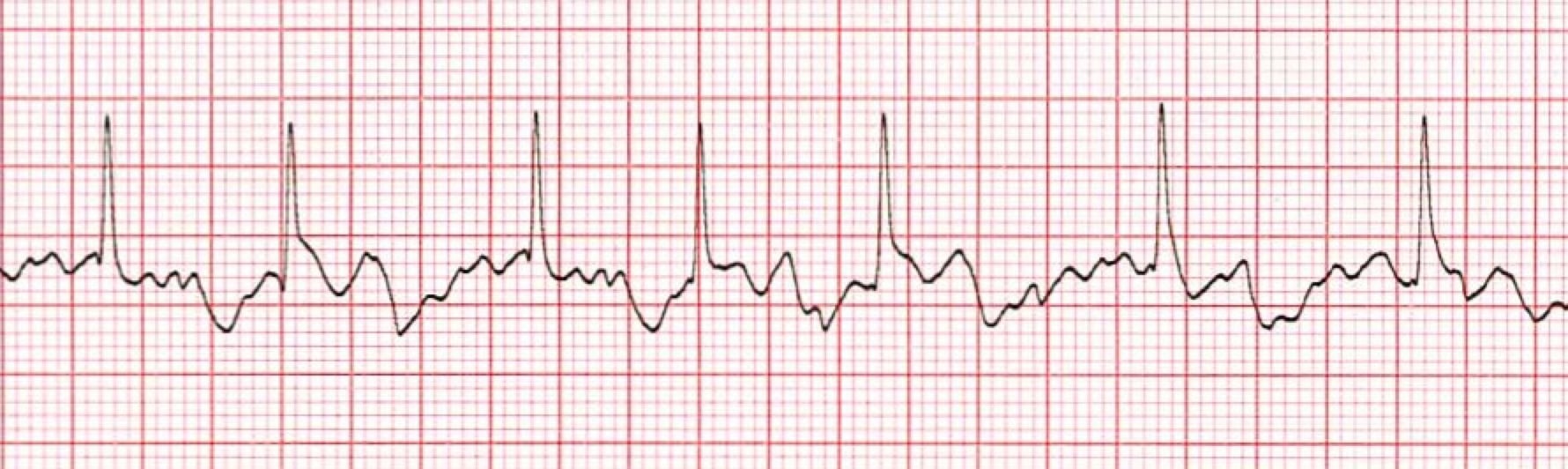 *Atrial Fibrillation ECG for Adult Patient
*Atrial Fibrillation ECG for Adult Patient
1. The Heart Rhythm
The first thing you'll want to look at is the heart rhythm. Does the heart rhythm look regular? Or does it look irregular? In the ECG above, the rhythm is irregular.
2. The Heart Rate
Next, you'll want to look at the heart rate of the patient. What is the patient's heart rate? Is it normal? Or is it too slow or too fast? In this case, it's 80 beats per minute, which is within normal range, but it's also variable because of its irregularity.
3. P-Wave
After looking at the heart rate, check to see if the patient's P-waves look normal by asking yourself the following few questions.
- Are the patient's P-waves present? No!
- Do they occur regularly? The answer is obviously no again.
- Is there one P-wave for each QRS complex? No.
- Are the P-waves smooth, rounded, and upright? No, only fibrillatory waves are present.
- Do all the P-waves have a similar shape? Again, that answer is no, because they aren't present.
4. PR Interval
Next, look at the PR interval on the patient's ECG readout and ask yourself the following questions:
- Is the PR interval normal, meaning between .12 and .20 seconds or is it contained within one large square on the readout? The answer is no, because there isn't a PR interval.
- Is the PR interval constant? Again, this in non-applicable since there isn't a P-wave.
5. QRS Complex
The last thing you should look at to determine if the sinus rhythm is normal or not is the QRS complex and ask yourself these questions while you do:
- Is the QRS interval less than .12 seconds? Yes, it is within the normal range.
- Is the QRS complex wide or narrow? In this case, it's narrow.
- Are the QRS complexes similar in appearance or are there noticeable differences? In this case, we can see that each looks similar.
So, what is your cardiac interpretation? Based on these questions and on the findings from the ECG readout above, it would appear that this patient is in atrial fibrillation.
- We have an irregular rhythm.
- We have a rate that is 80 beats per minute but also variable/irregular.
- The P-waves are missing.
- There is no PR interval.
- The QRS is less than .12 seconds and thus normal.
Common Causes and Side Effects of AFib in Adult Patients
The causes of AFib are numerous, but some common underlying reasons for it are:
- Congestive heart failure
- Previous history of damage to the SA node
- Conductive system dysfunction, from either current or past myocardial infarction
- A traumatic injury
- An underlying disease
- Past or present use of harmful drugs
- A metabolic disorder
Common side effects of AFib include but aren't limited to:
- A higher risk for coronary, cerebral, or pulmonary embolism and as a result of the increased potential for microemboli to develop, secondary to the lack of circulation of blood from the atria.
- Rapid ventricular response which can accelerate the ventricular rate to above 100 beats per minute.
- AFib combined with higher ventricular rates may decrease the amount of blood ejected from the heart due to the lack of, what is sometimes referred to as, the preloading atrial kick.